1. The role of the reed
The function of the reed is to determine the density
of the warp wires and the width of the net, to guide
the sword belt through the weaving mouth, and to
beat the weft wires towards the weaving mouth to
complete the weft beating movement.
2. Technical requirements of the reed process
(1) Reeds should be straight, evenly arranged, clear
and bright between the reed teeth, no soft pieces,
bruises, scratches.
(2) The reed surface of reed blade and tie wire is not
allowed to have corrosion phenomenon, the surface
is smooth without cracks and burrs, the edges are
not allowed to have sharp edges and corners, and
the reed surface is flat without high and low teeth.
(3) Reed density and the range of large reed holes
are measured and tested in accordance with product
technical requirements.
3. Types and structure of reeds
There are three kinds of reeds: welded reed, adhesive
reed and combination reed. Among the welded reeds,
there are tin-welded reeds and plastic-welded reeds,
and most of the domestic wire mesh is commonly used
as adhesive reeds.
A glued reed is a wire that is evenly wrapped between
two reed edges and coated with a layer of adhesive glue,
as shown in Fig. 3-9.
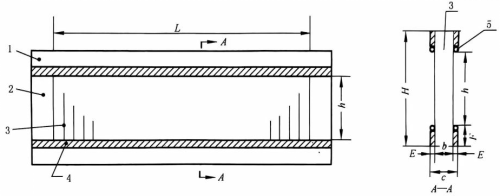
b -- reed width; c -- full width; h -- working height; L -- working length; H -- full height;
1 - Reclining Frames (ExF); 2 - Standing Frames; 3 - Reeds; 4 - Ties; 5 --Half Dollar Iron.